1. Hyper-V
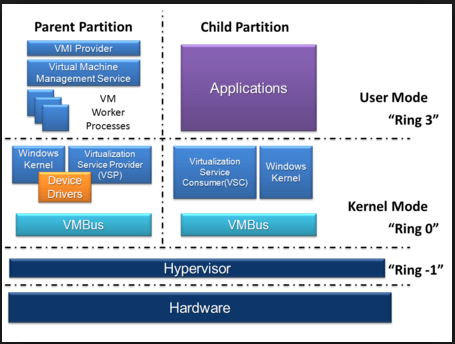
Microsoft Hyper-V, which was released in 2008, helps extend or create a private cloud network. This encourages effective hardware use, enhances business continuity and increases the quality of development and testing
Features of Microsoft Hyper-V for Windows Server 2019:
- Persistent memory support.
- Shielded VM updates.
- Simple Two-Node clusters.
- ReFS Deduplication.
- Storage Spaces Direct improvements.
- Windows Admin Center.
- Encrypted subnets.
2. KVM
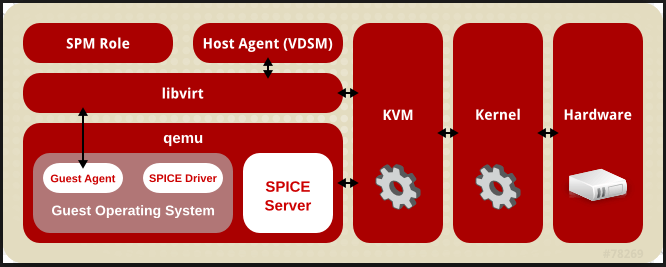
KVM is a Red Hat Virtuality Suite member and is a total virtualization architecture solution. It is an integrated virtualization system. KVM converts Linux to a hypervisor kernel. In version 2.6.20, it was merged into the mainline Linux kernel.
Features of Red Hat KVM:
- Container support
- Scalability
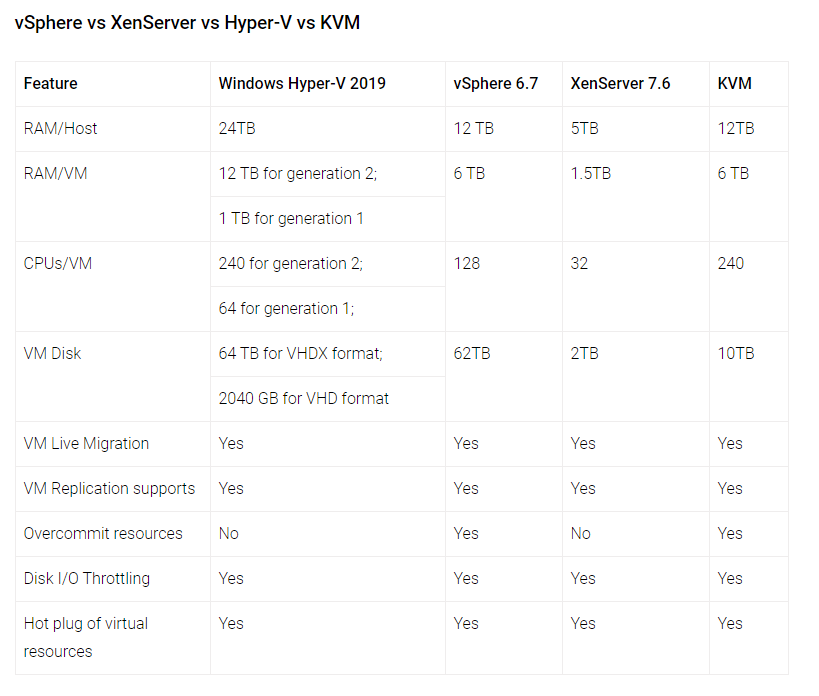
- Overcommit resources
- Disk I/O throttling
- Hot plug of virtual resources
- Low-cost virtualization solution
- Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization programming & API
- Live Migration & Storage Migration
- Assign any PCI device to virtual machines
- Red Hat Satellite integration
- Disaster Recovery support
3. vSphere
A collection of products including not only virtualization, but also control and inter-face layers, VMware virtualization platform vSphere. It provides various key elements (vCompute, vStorage, vNetwork), application services, vCenter Server, vSphere Client and so on.
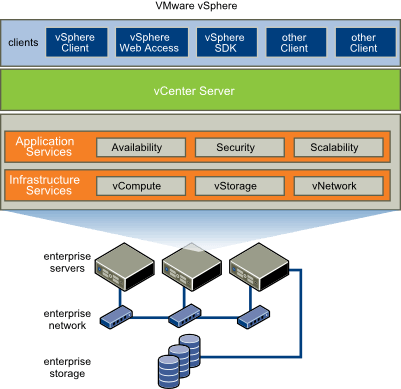
Features of VMware vSphere:
- vCenter Server: A centralized management tool used to configure, provision and manage virtual IT environments.
- vSphere Client: vSphere 6.7 has the final version of Flash-based vSphere Web Client. Newer workflows in the updated vSphere Client release includes vSphere Update Manager, Content library, vSAN, Storage policies, Host profiles, VMware vSphere Distributed Switch™ topology diagram and Licensing.
- vSphere SDKs: Provides interfaces for third-party solutions to access vSphere.
- VM File System: Cluster file system for VMs.
- Virtual SMP: Enables a single VM to use multiple physical processors at a time.
- vMotion: Enables live migration with transaction integrity.
- Storage vMotion: Enables VM file migration from one place to other without service interruption.
- High Availability: If one server fails, VM is shifted to other server with spare capacity to enable business continuity.
- Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS): Assigns and balances compute automatically across hardware resources available for VMs.
- Fault Tolerance: Generates copy of primary VM to ensure its continuous availability.
- Distributed Switch (VDS): Spans multiple ESXi hosts and enables considerable reduction of network maintenance activities.
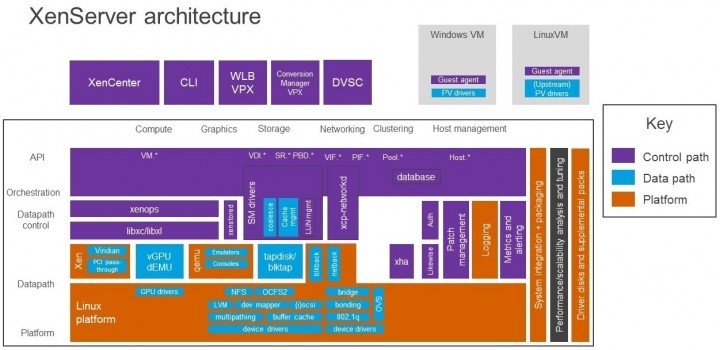
4. XenServer
XenServer is an open source bare-metal virtualization platform based on Xen Project Hypervisor. It contains business class features which help firms manage workloads, combined operating systems and networking settings easily. XenServer provides NIVIDA and Intel with enhanced virtualized graphics and allows many computer operating systems to be implemented on the same computer hardware.
Features of Citrix XenServer:
- Site Recovery
- Host Failure Protection
- Multi-server management
- Dynamic Memory Control
- Active Directory Integration
- Role Based Administration and Control (RBAC)
- Mixed Resource Pools with CPU Masking
- Distributed Virtual Switch Controller
- In Memory read caching
- Live VM migration & Storage XenMotion