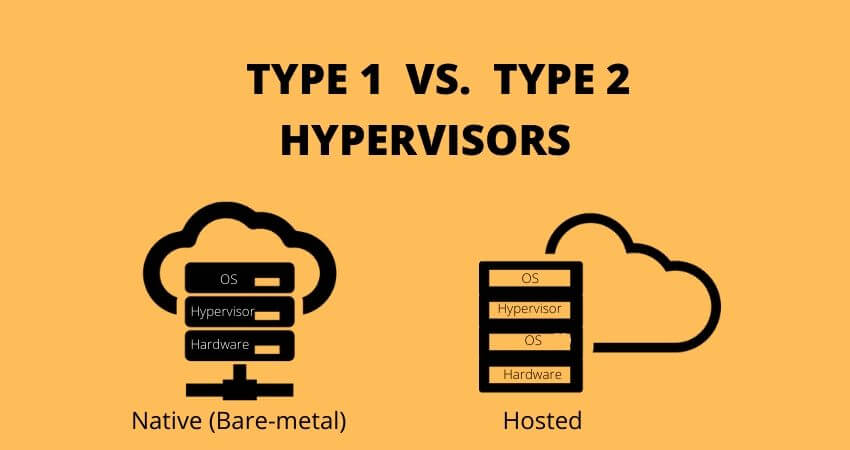
Type 1 hypervisors:
VMware ESX and ESXi
Like hypervisors are sophisticated and scalable, but need licenses to increase costs. VMware provides some lower-cost packages and can make hypervisory technology for small infrastructures more accessible. For Type-1 hypervisors VMware is a pioneer. You will buy your vSphere / ESXi software in a free version of 5 business editions.
Microsoft Hyper-V
Secondly, the HyperVisor from Microsoft, Hyper-V, doesn’t offer many of VMware products ‘ advanced features. Hyper-V is however one of the top 3 type-1 hypervisors with XenServer and vSphere. It first came out with Windows Server, but now with Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V, it’s Hyper-V. Hyper-V is included in the four commercial versions-Foundations (OEM only), Essentials, Standard, and Datacenter (not GUI or virtualization rights).
Citrix XenServer
It originated as a project open source. The main hypervisor technology is free, but it has almost no advanced features like VMware’s free ESXi. Xen is a hypervisor of form 1 bare metal. Just as the virtualization system used by Red Hat Enterprise uses KVM, Citrix also uses Xen in the XenServer.
Currently, projects and groups in the open source Xen are on Xen.org. Today, XenServer is a 4-edition commercial hypervisor Type-1 solution from Citrix. Citrix has also confusedly branded its own proprietary XenApp solutions such as XenApp and XenDesktop.
Oracle VM
The hypervisor of Oracle is based on Xen. Nonetheless, you’ll have to pay for supporting hypervisors and software updates. Oracle VM lacks many of the advanced features in other hypervisors for bare metal virtualization.
Type 2 hypervisors:
VMware Workstation/Fusion/Player
A free hypervisor is VMware Player. It is designed to run only one VM and does not require VMs to be create. VMware Workstation is a more stable hypervisor with some advanced features such as recording and playback and support for VM snapshot. It has three main uses: various operating systems or one-off versions of an operating system running on the same desktop, developers needing sandbox environments and screenshots, and laboratories and demos.
VMware Server
The VM is a free, hosted hypervisor for virtualization very much like the VMware Workstation. Since 2009, VMware has suspended software growth.
Microsoft Virtual PC
This is the latest version of Windows Virtual PC, which operates on Windows 7 and only supports Windows operating systems that run on the hypervisor technology.
Oracle VM VirtualBox
If you want a budget to virtualise, VirtualBox hypervisor technology offers you reasonable performance and features. While being open, host, VirtualBox shares many characteristics with VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V, with its very small footprint.
Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization
The Kernel Virtual Machine of Red Hat (KVM) has host and bare-metal virtualizing hypervisor qualities. The Linux kernel itself can become a hypervisor, so that the VMs can access the physics hardware directly.
KVM
This is a Linux kernel virtualization facility. It supports native virtualization on hardware virtualization extension processors. The open-source virtual machine (KVM) can be applied to most Linux operating systems like Ubuntu, Debian, SUSE, and Red Hat Enterprise, as well as Solaris and Windows. Therefore, the KTM is a Linux based type-1 hypervisor.